Unnatural links are links that are created or obtained in a way that violates Google’s guidelines and best practices. They are often used to manipulate the search engine rankings of a website or a web page.
They can have a negative impact on your website’s SEO, as Google can penalize your site for having them. In this guide, we will explain what unnatural links are, how to identify them, how to find them, and how to fix them.
What are Unnatural Links?
Unnatural links are links that are not earned naturally by providing valuable content or service to your users. They are usually created or obtained by using link schemes, such as buying or selling links, exchanging links, using automated programs or services, participating in low-quality directories or blog networks, and similar.
Unnatural links can also be created by over-optimizing your anchor texts, hiding or cloaking your links, placing your links in irrelevant or low-quality sites, etc.
Unnatural links are harmful for your SEO because they violate Google’s quality guidelines, which state that:
Any links intended to manipulate PageRank or a site’s ranking in Google search results may be considered part of a link scheme and a violation of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. This includes any behavior that manipulates links to your site or outgoing links from your site.
Google can detect unnatural links by using its algorithms or by manual reviews. If Google finds unnatural links pointing to your site, it can apply a manual action or an algorithmic penalty to your site, which can result in lower rankings, less traffic, or even de-indexing of your site.
How to Identify Unnatural Links
The first step to finding and fixing unnatural links is to identify if your site has been affected by them. There are two ways to check if your site has been penalized by Google for having unnatural links: manual actions and algorithmic penalties.
Manual Actions
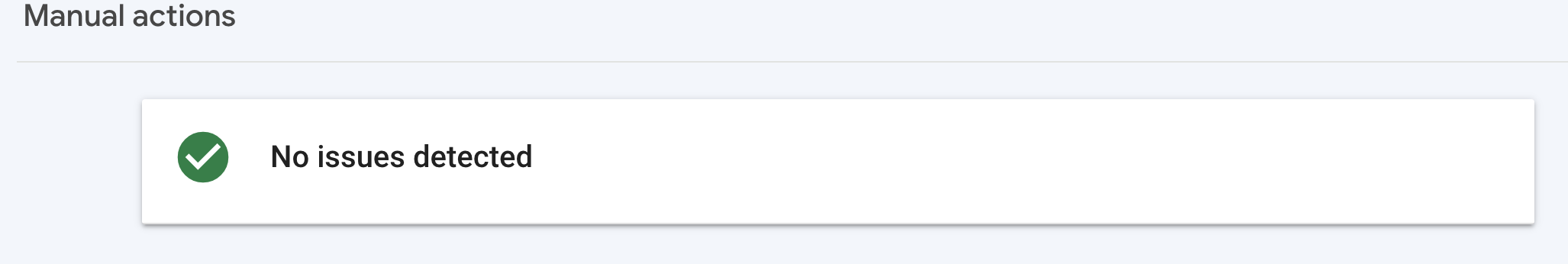
Manual actions are when Google’s human reviewers manually apply a penalty to your site for violating the quality guidelines. You can check if your site has a manual action by using Google Search Console. To do this, follow these steps:
- Log in to your Google Search Console account and select your site.
- Click on Security & Manual Actions > Manual Actions.
- If you see a message that says “No issues detected”, then your site does not have a manual action.
- If you see a message that says “Manual Actions report”, then your site has one or more manual actions. Click on the message to see the details of each manual action, such as the type, the reason, the affected pages or links, and the date.
Some common types of manual actions related to unnatural links are:
- Unnatural links to your site: This means that Google has detected unnatural links pointing to your site from other sites. You need to remove or disavow these links.
- Unnatural links from your site: This means that Google has detected unnatural links pointing from your site to other sites. You need to remove these links.
- Thin content with little or no added value: This means that Google has detected low-quality content on your site that provides little or no value to your users. You need to improve or remove this content.
Algorithmic Penalties
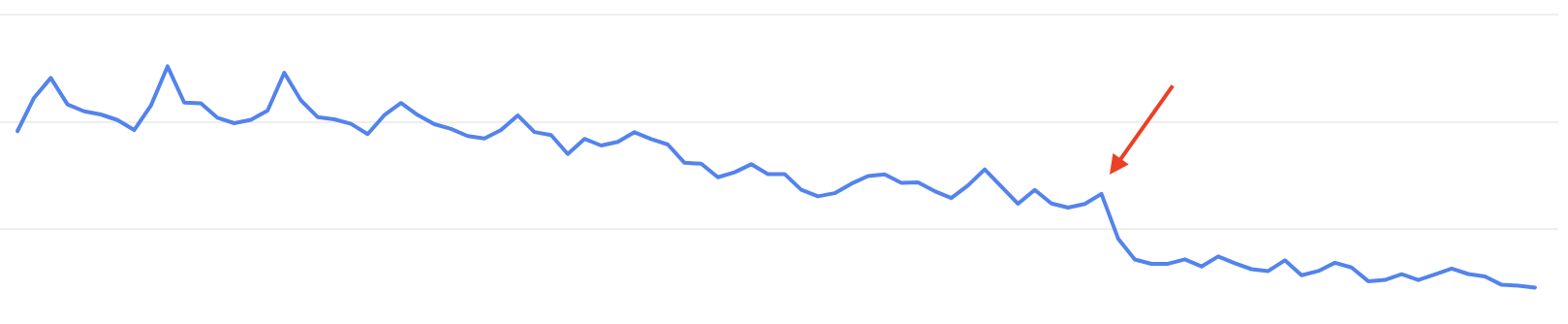
Algorithmic penalties are when Google’s algorithms automatically apply a penalty to your site for violating the quality guidelines. You cannot check if your site has an algorithmic penalty by using Google Search Console, but you can use other tools or methods to detect them. Some common signs of algorithmic penalties are:
- Sudden drops in rankings, traffic, or conversions: This means that Google has lowered the ranking of your site or some of your pages for certain keywords or queries. You need to find out which keywords or queries are affected and why.
- Changes in search results: This means that Google has changed the way it displays the search results for certain keywords or queries. You need to find out which keywords or queries are affected and how they have changed.
- Notifications from third-party tools: This means that some tools that monitor your site’s performance or SEO have detected changes in your site’s metrics or indicators. You need to check which tools have notified you and what they have reported.
Some common types of algorithmic penalties related to unnatural links are:
- Penguin: This is an algorithm that targets sites that use unnatural link schemes or over-optimize their anchor texts. It was launched in 2012 and became part of the core algorithm in 2016.
- Panda: This is an algorithm that targets sites that have low-quality content or user experience. It was launched in 2011 and became part of the core algorithm in 2016.
How to Find Unnatural Links
The next step to finding and fixing unnatural links is to audit your link profile and find the unnatural links that are pointing to or from your site. In this guide, we will use Ahrefs as an example, but you can use any tool that suits your preferences or budget.
To find unnatural links using Ahrefs, follow these steps:
- Log in to your Ahrefs account and enter your site’s domain in the search bar.
- Click on Site Explorer > Backlinks > Referring Domains.
- You will see a list of all the domains that are linking to your site, along with some metrics, such as Domain Rating (DR), Ahrefs Rank (AR), Number of Backlinks, Number of Referring Pages, etc.
- You can sort or filter the list by using the options on the top or the left side of the page. For example, you can sort by DR or AR to see the most or least authoritative domains, or you can filter by language, country, platform, etc. to see the most or least relevant domains.
- You can also use the search bar on the top right corner of the page to search for specific keywords or phrases in the domain names or anchor texts. For example, you can search for “buy”, “sell”, “exchange”, “directory”, “blogspot”, “forum”, etc. to find potential link schemes or low-quality sites.
- You can click on any domain name to see more details about it, such as its backlink profile, its organic traffic, its top pages, etc. You can also click on any backlink or referring page to see more details about it, such as its anchor text, its surrounding text, its URL rating (UR), its traffic, etc.
Some criteria for evaluating the quality and relevance of your backlinks are:
- Domain Rating (DR): This is a metric that measures the authority and popularity of a domain based on the quality and quantity of its backlinks. The higher the DR, the more authoritative and trustworthy the domain is. Generally, you want to have backlinks from domains with high DR, as they can boost your site’s authority and ranking. However, you also need to consider other factors, such as relevance and diversity.
- Anchor Text: This is the clickable text that is used to link to your site or page. The anchor text should be relevant and descriptive of your site or page’s content and purpose. It should also be natural and varied, as using the same or over-optimized anchor texts can indicate unnatural link building or manipulation. Generally, you want to have backlinks with anchor texts that match your target keywords or phrases, but not too much or too exact.
- Link Location: This is the place where your link is located on the referring page. The link location should be relevant and contextual to your site or page’s content and purpose. It should also be visible and accessible to your users and search engines. Generally, you want to have backlinks that are located in the main content area of the referring page, rather than in the footer, sidebar, header, navigation menu, etc.
- Link Relevance: This is the degree of similarity or connection between your site or page and the referring site or page. The link relevance should be high and meaningful for your site or page’s content and purpose. It should also be beneficial and useful for your users and search engines. Generally, you want to have backlinks from sites or pages that are related to your niche, industry, topic, audience, etc.
Here are two examples where we found unnatural links using “blogspot” and “forum” filters:
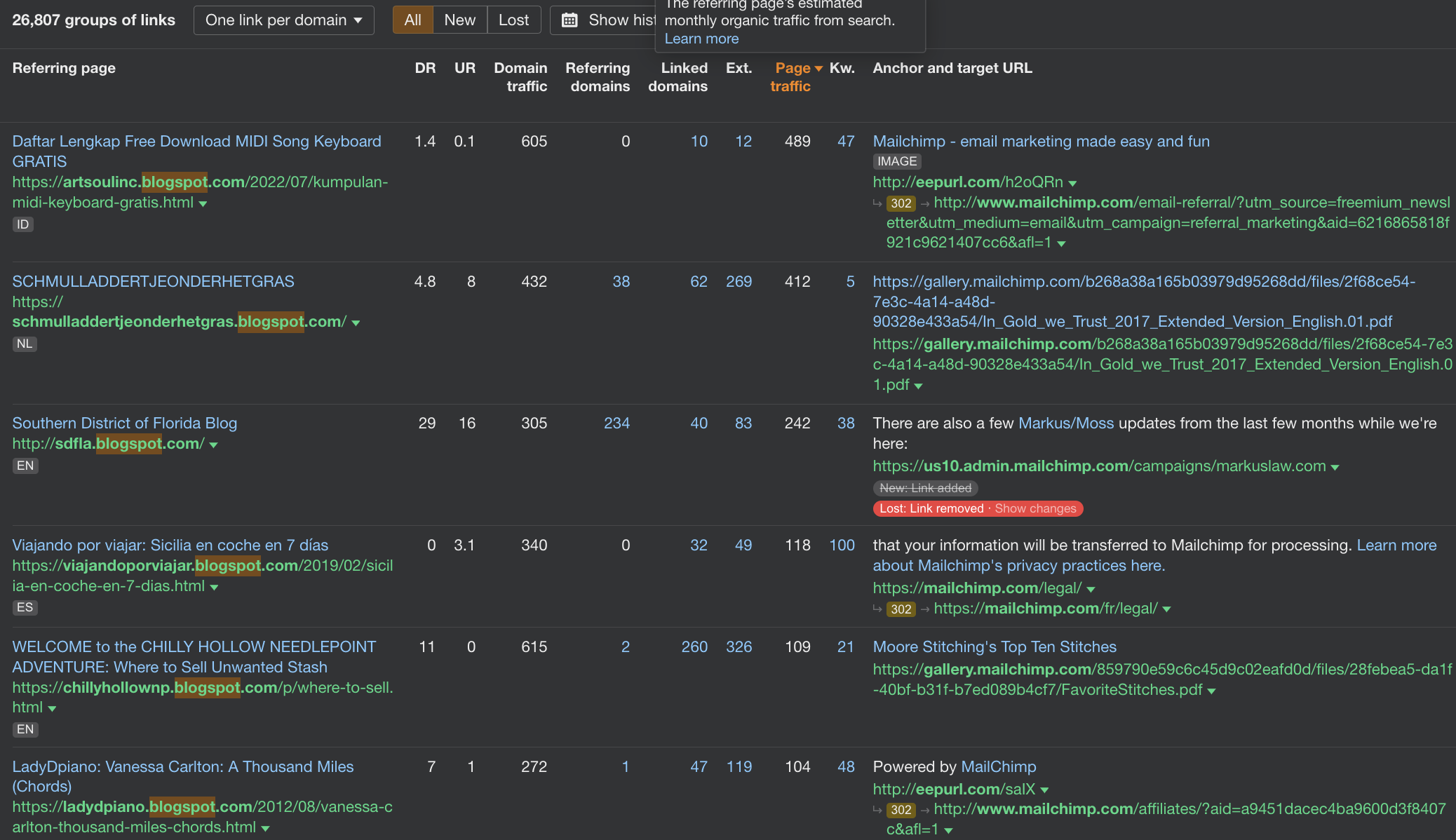
There are 10k+ links with the “blogspot” type of domain here, which usually have little value because of:
- Low DR
- Low relevancy
- Low domain traffic
- Spammy anchor text usage
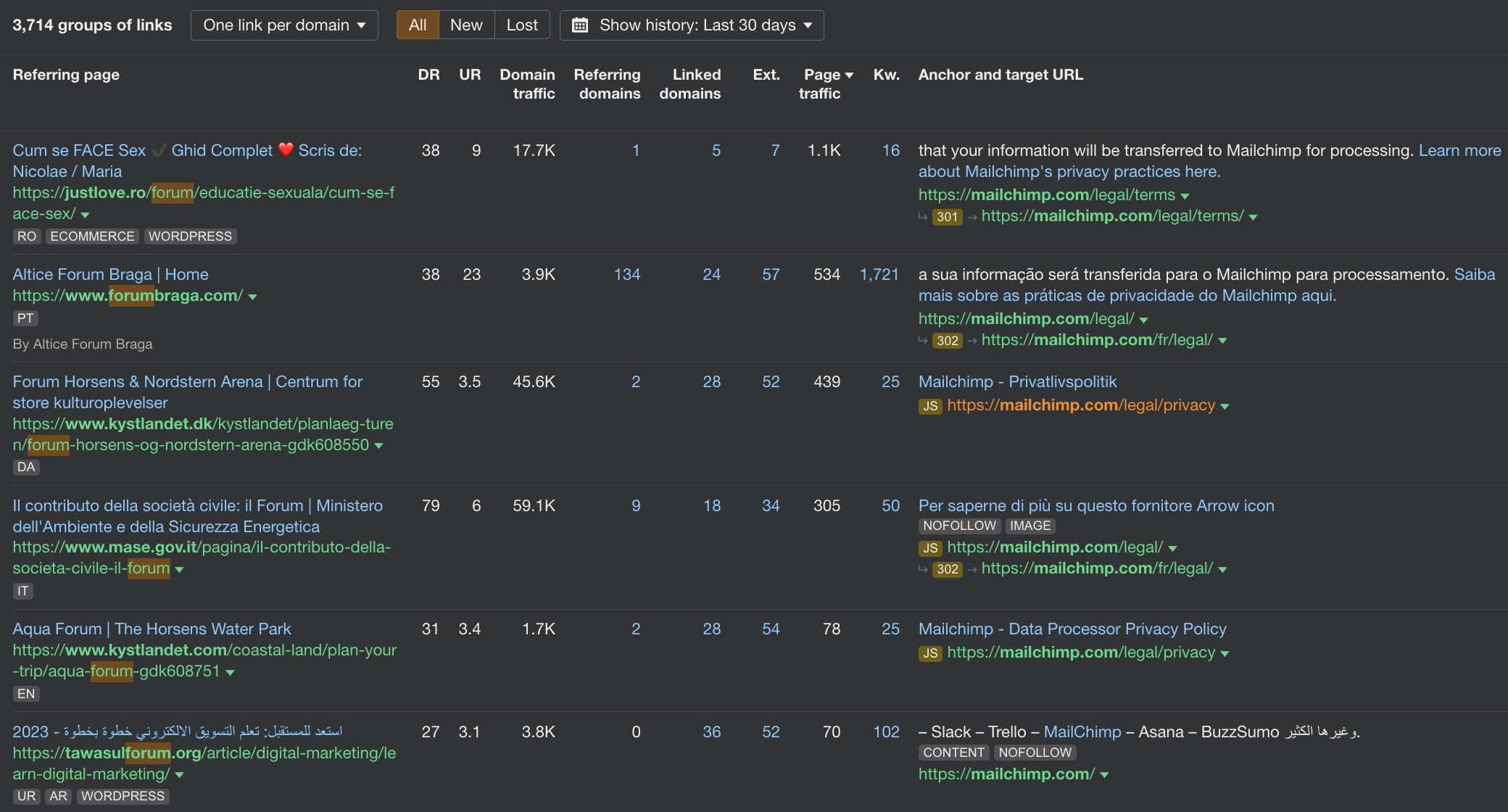
While forum links might sound great on paper because of their metrics, don’t get fooled by them – they are usually low-quality links, because of:
- No-follow attribute
- Use spammy anchor text
- Usually not relevant to your niche
- Might come from NSFW niches as well
How to Fix Unnatural Links
The final step to finding and fixing unnatural links is to remove or disavow them using Google Search Console. To do this, follow these steps:
- Go to Disavow links tool and choose your property.
- You will see a message that warns you about the risks of using this tool. Read it carefully and click on Disavow Links again.
- You will see a message that asks you to upload a file with the links you want to disavow. Click on Choose File and select a text file (.txt) from your computer.
- The text file should contain one link per line. You can use “#” to add comments. You can disavow individual links or entire domains by using “domain:” before the domain name.
- Click on Submit to upload your file and disavow the links.
- You will see a message that confirms that your file has been uploaded and processed. It may take some time for Google to crawl and re-evaluate your links, so be patient and monitor your site’s performance and metrics.
Wrapping Up
By following these steps, you can find and fix unnatural links that hurt your SEO. Remember that unnatural links are not only bad for your site’s ranking and reputation, but also for your users’ experience and trust.
Therefore, you should always aim to build natural and high-quality links that provide value and relevance to your site and your users.